Products
Products by Name
Click a product name to jump to the product details section of the page.
Low-pressure casting molds
[Low-pressure die casting] (Commonly known as: LP molds, low pressure casting)
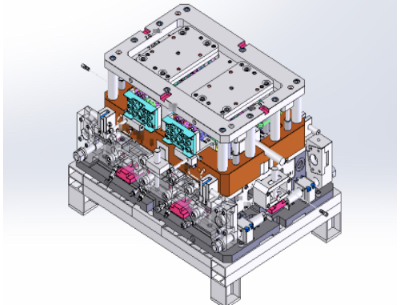
As its name suggests, low-pressure die casting is a process in which molten metal, such as aluminum alloy, is injected at a low pressure and speed.
An advantage of this casting method is that it yields a highly airtight product with a lower level of gas trapped in the casting because of the gentle flow of molten metal inside the mold.
Another advantage of low-pressure die casting is that it can produce products with complex or hollow shapes by using a compacted sand core, which is collapsed after casting.
On the other hand, disadvantages include filling defects due to the low pressure and speed of the molten metal injection, which makes it generally unsuitable for thin-walled shapes.
Another disadvantage is the longer casting cycle.
Low-pressure casting is mainly used for cylinder heads and aluminum wheels in automobile parts.
Gravity casting molds
[Gravity die casting] (Commonly known as: GDC, GDC molds, gravity casting)
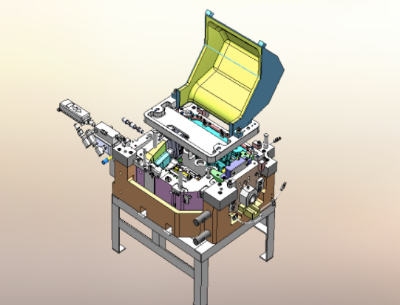
Gravity casting is a process in which molten metal, such as aluminum alloy, is injected into a mold from a supply port provided at the top of the mold by the force of gravity alone, without applying external pressure.
The advantages of gravity casting include relative freedom for setting the conditions for the casting method, and, like low-pressure die casting, its ability to produce products of a complex or hollow shape by using a compacted sand core, which is collapsed after casting.
Disadvantages include the possibility of filling defects because using gravity to pour the molten metal makes it difficult to adjust injection and filling speeds. Another defect is the likelihood of oxide being trapped because ladles are used for pouring.
The injection speed can sometimes be addressed with tilting gravity die casting, in which the mold is tilted to adjust the speed.
Gravity die casting is mainly used for steering knuckles and crankcases in automobile parts.
Sand casting molds
[Green sand mold casting] (Commonly known as: sand molds, green sand molds)
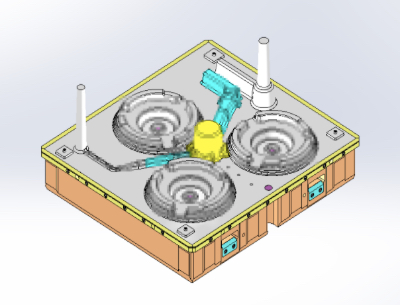
Sand mold casting is a process in which silica sand mixed with additives is compacted using two or more upper and lower molding flasks to form sand molds with negative impressions of the flasks. Then, these sand molds are mated and molten metal is injected.
An advantage of using sand molds is their lower initial cost, as they do not require large equipment. They are also suitable for checking castings in the study stages before mass production—for example, in trial production—and for small-lot production.
Sand mold casting is also used to cast complex shapes and large castings.
A disadvantage of sand mold casting is that, compared to mold casting, the casting surface is rough and the dimensional accuracy is inferior.
The running cost is also high because for each casting, the sand mold needs to be broken to take out the product.
Sand mold casting is mainly used for brake drums and flywheels in automobile parts.
Die casting molds
[High-pressure die casting] (Commonly known as: HPDC, die casting, die-casting, DC molds)
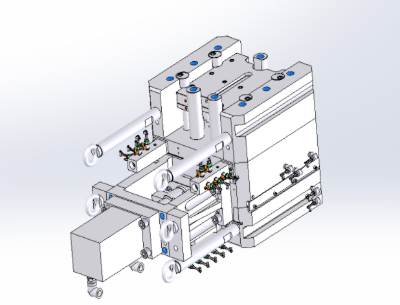
Die casting is a process where molten metal, such as aluminum alloy, is injected into a fine mold under high pressure.
The advantage of using this casting method is its suitability for making thin-walled products because the molten aluminum flows into the mold at a high speed and pressure, making it possible to form castings with high surface precision.
The casting cycle is also short, making it suitable for large-volume production.
A disadvantage is that the air inside the mold and the gas emitted from the mold release agent are also trapped in the castings during the process, so the mechanical strength of the casting is inferior, making it unsuitable for parts requiring rigidity.
Die casting molds are also more expensive than other casting molds because they require higher precision and strength.
The larger the production volume, the greater the advantage, but it is not suitable for small-lot production.
Die casting is mainly used for cylinder blocks, cases, and covers in automobile parts.
Core-making molds
[Sand core boxes, sand core molds] (Commonly known as: cores, core molds)
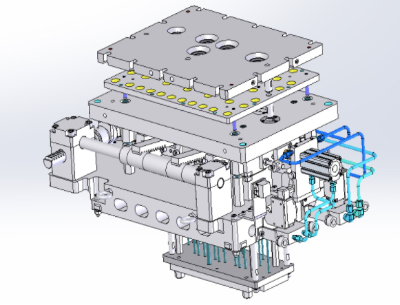
There are several processes for core molding. Shell molding, which is used mainly for casting, gets its name because it is casted by taking two sand shells obtained by blowing silica sand coated with thermosetting resin, putting them together like two halves of a seashell, and hardening them in a heated mold.
It allows a finer casting surface than sand mold casting, which is a self-hardening process, making finishing work easier.
The shell molding process is not only used for making sand molds for casting but also to make sand cores to create a hollow space in castings by low-pressure casting, gravity casting, or sand casting.
The mold is heated by gas or electric heaters.
It may also use the cold box process—which uses organic, ordinary-temperature gas for curing—and molds made of inorganic water glass (commonly called “inorganic cores”).
